A wide range of equipment for tone rail circuits (TRC) and ALS coding produced by NPP KS-MISAT LLC allows you to implement a functionally complete subsystem for monitoring and coding rail circuits with the reception and transmission of information through a digital and/or relay interface, diagnostic measurements of the electrical signals of the TRC, as well as continuous monitoring of the working condition of the devices included in it.
The equipment of the “NPP KS-MISAT” is used in station and outstation systems of railway automation with centralized and decentralized placement of equipment.
The subsystem of control of rail circuits with equipment "NPP KS-MISAT" allows you to provide:
- control of the free and busy sections, the integrity of rail threads and the transmission of information to microprocessor and relay systems of automatic blocking and electrical centralization;
- the formation and transmission of ALSN/ARS signals to rail circuits;
- automatic diagnosis of the state of the devices included in its composition, with the registration of failures;
- data exchange with signaling microprocessor systems via a digital interface (RS-422, Ethernet, etc.);
- the formation of analog control signals of electromagnetic relays and monitoring (polling) of the tee contacts of the relay (when linked to relay systems of signaling systems);
- formation of a “malfunction” signal when deviating from the normalized values of active resistance “signal pair - signal pair”, “signal pair - ground”, as well as the integrity of the wires in the transmission cables of signals of tone rail circuits.
The use of tonal rail chains in comparison with code and phase-sensitive rail circuits has the following advantages:
- it is possible to lay an all-welded railway track between stations without using insulating joints on the hauls, which account for about a large part of the failures of equipment of railway automation systems;
- a significant reduction in the use of throttle transformers in electrified areas, which helps to reduce failures due to breakage and theft of jumpers and maintenance costs;
- the placement of the equipment TRC at the stations gives an improvement in the service conditions of the equipment and reduces the time for eliminating failures by reducing the cost of arrival time at the place of failure;
- are applied at any types of draft;
- reduction of electricity consumption;
- lack of contact relays, which significantly increases the reliability and durability of the equipment;
- high immunity to traction current interference.
The use of tonal frequency rail circuits is preferred:
- For all station rail circuits for all types of traction to reduce power consumption and protect against traction current interference;
- To control the freedom of haul and serviceability of rails in the system of semi-automatic blocking (PAB) - in addition to improving the safety of train traffic, this allows the implementation of centralized dispatch systems;
- For equipment in coding and pulse-wire AB protection areas of the required length without additional installation of relay cabinets and high-voltage linear transformers;
- To obtain the necessary length of the sections of the approach to the move, which allows to minimize the premature closure of the move;
- In areas with reduced ballast resistance.
The composition of the subsystem for monitoring the track sections is selected according to customer requirements.
The subsystem for monitoring sections can be performed with hot redundancy of equipment and duplication of communication channels, which increases operational reliability, which is subject to increased requirements on metro lines and trunk transport. Hot standby allows switching to standby in case the redundant module goes into protective state.
The use of the rail-circuit monitoring subsystem with the NPP KS-MISAT equipment reduces the switching time when replacing the relay systems of the electronic modules with the MPC due to the possibility of controlling the operation of the modules at the first stage through the relay interface, and at the second stage - switching to control via the digital interface without additional switching installation of equipment of rail chains and coding.
The tonal rail circuit subsystem and the ALS \ ALSN coding subsystem can be used both jointly and separately, depending on the need at a particular station. For example: tonal rail chains without coding or ALSN coding in areas with an axle counting system without a TRC.
The tonal rail circuit subsystem works with the standard range of frequencies of the SEC3-SEC4 and can be released on request for other operating frequencies.
The ALS coding subsystem provides coding of sections at frequencies of 25, 50 and 75 Hz for trunk transport, and at frequencies of APC (75, 125, 175, 225, 275 and 325 Hz) for the subway. Changing the coding frequency is done without installing additional equipment.
Linking with top-level systems is done by docking via digital interfaces or rail circuits using the Logical Dependency Controller and the gateway to the MPC-TRC KLTRC-LINK MPC. Entering the state of the relay is done using the MK-TOS.32.6 Safe Input Module. The inclusion of interface or trip relays is provided by the MK-TOU16.6 Safe Output Module.
The equipment TRC is available in 6U version for installation in 19 ”racks. There are two modifications TRC equipment:
- Tone frequency generator GFPU.3.420-780 and tone rail receiver PTRC.5.420-780.RO modules with built-in input / output filters and power supplies.
- Modules six-channel tone rail circuit generator MK-GFPU.6 and tone rail receiver MK-PTRC.10 with external filters Track Filter for tone rail generator FPU.3.420-FPU.3.780 and Track Filter for tone rail circuit receiver FP .5.420-FP.5.780.
Both versions of the TRC are functionally similar, compatible and selected by the customer depending on the specific conditions of use at the station.
A significant advantage of the rail chain monitoring subsystem with the NPP KS-MISAT equipment is the high density of the equipment of the TRC due to its small size compared to the equipment of the 3rd and 4th generation of the TRC with placement on relay racks. The equipment of the “NPP KS-MISAT” is located in crates in 19 ”general industrial electrical cabinets.
In one cabinet 2200x600x600mm (48U) you can place the equipment of the TRC and coding without hot backup in the amount:
- 72 generator ends of the RC;
- 120 receiving ends of the RC;
- 120 coding points on MK-GALS.8;
- 32 coding points on MK-GALS.2;
- 32 ARS points on MK-GARS.2.
When using hot standby, one 2200x600x600mm (48U) cabinet place the equipment of the TRC and coding in quantity:
- 36 generator ends of the RC;
- 60 receiving ends of the RC;
- 60 coding points on MK-GALS.8;
- 16 coding points on MK-GALS.2;
- 16 ARS points on MK-GARS. 2.
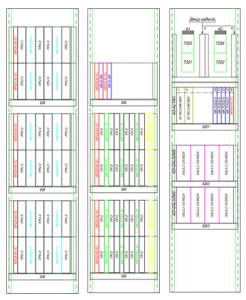
An example of layout of cabinets of generators and receivers of a TRC, coding
Depending on the number of arrows and signals at the station, the configuration of the cabinets is determined. With a small number of shooters at the station, it is possible to install ALSN generator cassettes in the cabinet TRC generators.
It is preferable to place the receivers and generators TRC in different cabinets to prevent accidental confusion of the generator and relay ends of the rail circuits during operation, but is allowed.
MK-GFPU.6
Six-channel tone frequency track circuits generator

Specifications:
- Power supply voltage - 24V DC
- Dual-channel safety architecture
- Isolation between the channels and between the control electronics and the output of 3kV
- It works through a passive track filter FPU.3.420- FPU3.780 that allows you to get a classic load curve when a train ocupies a track circuit, and also provides generator survivability
- Continuous measuring of the output signal parameters to detect emergency operation and protective shutdown
- The built-in mechanical complete disconnect relay allows you to reliably disconnect the generator when an emergency operation is detected from the track circuit, and also allows for hot standby
MK-PTRC.10
Group receiver tone frequency track circuits

Specifications:
- Dual-channel safety architecture with hardware comparison unit
- Monitors up to 10 receiver ends of AFTC
- Information on all channels passes through the safety hardware “AND”-unit
- The operation algorithm is completely analogous to the actions of an analog receiver, it takes into account both the amplitude and modulation depth of the input signal
- It passes information about the input voltage, modulation depth hardware errors
- Settings are stored in external flash memory chips on each channel, before starting the configuration are compared
- Works together with track filters of type FP.5.420-FP.5.780
FPU.3.420-FPU.3.780
Track filter for tone frequency track circuits generator

Specifications:
- One link passive output track filter for each channel
- Provides normalized output impedance at natural frequency and low impedance at other frequencies
- No recalculation of normals (requirements) required
- A failure of any filter element is determined with the transition to a protective generator failure
- Provides additional galvanic isolation and generator protection
- Increases system survivability
- Used together with a module MK-GP.6
FP.5.420-FP.5.780
Track filter for tone frequency track circuits receiver

Specifications:
- 5-channel two-link passive input line filter
- Provides normalized input impedance at natural frequency and low resistance at other frequencies;
- No recalculation of normals (requirements) required;
- A failure of any filter element is determined with the transition to the protective failure of the track receiver;
- Provides passing signal ALS, ARS and other frequencies of the AFTC
GFPU.3.420-780
Tone frequency signals generator

Specifications:
- Three independent generating outputs
- Built-in galvanically isolated DC/DC power supply
- Built-in passive track filters allow you to get a classic load curve when a train occupies a track circuit, and also provides generator survivability;
- Two-channel architecture
- Isolation between channels and also between control electronics and 3kV output
- Continuous measuring of the output signal parameters to detect emergency operation and protective shutdown
- The built-in mechanical complete disconnect relay allows you to reliably disconnect the generator when an emergency operation is detected from the track circuit, and also allows for warm standby
- Settings are stored in external flash memory chips on each channel, before starting the configuration are compared
PTRC.5.420-780.RO
Group receiver tone frequency track circuits

Specifications:
- Controls 5 receiver ends of the AFTC
- Built-in two-link passive input track filter per each channel
- Provides a normalized input impedance at its own frequency and low resistance at other frequencies to pass the signal current of ALS, ARS, AFTC
- No recalculation of normals (requirements) is required
- The failure of any filter element is determined with the transition to the protective failure of the receiver
- Built-in galvanically isolated DC/DC power supply
- Dual-channel safety architecture on signal processors with hardware comparison unit
- Information on all channels passes through the safety hardware “AND”-unit
- The operation algorithm is completely analogous to the actions of an analog receiver, it takes into account both the amplitude and modulation depth of the input signal
- It passes information about the input voltage, modulation depth, hardware errors
- Settings are stored in external flash memory chips, before starting the configuration are compared
MK-GALS.2.120.MS24/MK-GALS.2.120.MS220
MK-GALS.1.250.MS220
Track circuits code generator with two channels

Specifications:
- Two independent channels for signal generation with power up to120W per channel or modification with 1 channel up to 250W
- Signal generation at frequencies of 25, 50 and 75 Hz of a required amplitude and duration
- Provision the synchronization of codes of all generators at a station and a running line
- Power supply voltage - 24V DC or 220 AC
- Dual-channel safety architecture
- Implemented the ability of warm backup generators
- Isolation between the channels and between the control electronics and the output of 3kV
- In each channel, self-diagnosis of internal and output circuits
- Indication of the output signal on the LCD display
- Settings are stored in external flash memory chips on each channel, before starting the configuration are compared
MK-GALS.8
Track circuits code generator with eight channels

Specifications:
- Switching signal to 220V to 5A on each channel
- Providing the formation of signals with time parameters KPT-5 and KPT-7
- Provision the synchronization of codes of all generators at a station and a running line
- Power supply voltage - 24V DC
- Dual-channel safety architecture
- Implemented the ability of warm backup generators
- Isolation between the channels and between the control electronics and the output of 3kV
- The output of the generator is connected through solid-state relays with a safety “AND”-unit in its input
- In each channel, the measuring of the output voltage and output current
- Indication of the parameters of the output signal on the LCD display
- Settings are stored in external flash memory chips on each channel, before starting the configuration are compared
MK-GARS24.2
Automatic speed control signals generator with two channels

Specifications:
- Providing the formation of automatic speed control signals with frequencies 75-325 Hz
- Providing two outputs with voltage up to 90V and up to 100W per output
- Power supply voltage - 24V DC
- Dual-channel safety architecture
- Possibility of forming a two-frequency signal
- Implemented the ability of warm backup generators
- Repeats the load curve of an analog generator with a filter; when a train occupies a track circuit. It switches to the current stabilization mode (reducing the output voltage)
- Indication of the output signal on the LCD display
- Settings are stored in external flash memory chips on each channel, before starting the configuration are compared
MK-TOS.32.6
Safety input module

Specifications:
- Safety input of relay status
- Two groups of 16 control inputs each
- Principle of monitoring all three contacts of a relay contact group
- Dual channel safety architecture
- 6 CAN communication lines - 3 per CPU
- Direct independent communication with each operating controller;
- Galvanically isolated test code generator and galvanically isolated code reading to determine relay status
MK-TOU.16.6
Safety output module

Specifications:
- Safety switching on of 16 load channels (relays, etc.) with voltage 24V and current up to 42mA (1 W)
- Each channel is galvanically isolated from power and from each other
- Short circuit detection, load break, command execution control
- Monitoring the availability of output voltage
- Output current control
- Dual-channel safety architecture
- 6 CAN communication lines - 3 per CPU
- Direct independent communication with each operating controller
- Majorization of received commands before execution
- Unstabilized (“dirty”) 24V power supply can be used to control external relays